|
KNEE AND SURGERY
|
||
|
English version of the
website of Dr. J.E.Perraudin, french orthopaedic surgeon in paris
: www.docteurperraudin.com : the content is intended for general information
only and does not replace the need for personal advice from a qualified
health professional. Last updated Feb 12, 2017 |
||
Knee Osteotomies |
||
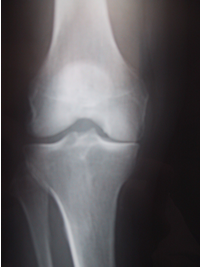
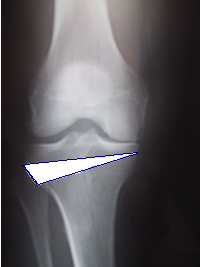
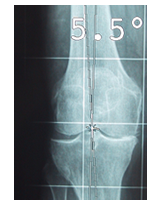
A knee osteotomy is to cut a bone (tibia or femur) to straighten the bone (in young people with a bow leg or a knock knee deformity) or to alter the line of weight bearing in case of arthritic joint. Osteotomy may be appropriate in patients under 60 years, who have moderate or severe wear on only one side of the joint.early arthritic joint as a result of injury. Those patients are usually less than 60 years old and too young for knee replacement. Long X-rays of both legs are needed to measure the exact degree of misalignment. This is essential for calculating the amount of correction needed before surgery. The most frequent case is arthritis limited to the inner compartment of the knee with deformity in varus (bow leg) : it is called a proximal tibial valgus osteotomy. The osteotomy consists in correcting the alignment of the leg to
take the weight out of the worn area and allowing it to be taken
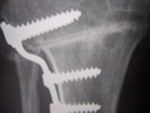
through the good part of the joint.. Osteotomy is performed by cutting the bone first. Then the deformity is corrected either by bending the bone into the correct position and holding it there with a plate and screws. A small piece of bone or synthetic bone can be place in the opening to help maintening the correction. Alternatively, a small piece of bone can be cut out of the bone and then to correct the deformity, the two cut edges are brought together and helded by a plate and screws. These metal implants can be left or removed later when the osteotomy has healed : it takes about three months to heal but the patient can put some weight on the limb quite early with crutches. Rehabilitation will take about three months. Dependly of how quickly you heal, you will need to walk with crutches for 2 to 4 months. Depending on the type of work you do, you can usually return to work after three to four months. Osteotomy will usually relieve the pain, stop the deformity and allow the patient to get back to some sporting activities which could not be possible with a knee joint replacement.There is a chance to eventually need unicompartimental or total knee replacement, which can be a more technically challenging procedure when you've had an osteotomy. Infections and other complications possible. Cosmetically, the knee may not look symetrical after osteotomy.
Docteur Jean Etienne Perraudin, last updated 1 09 2012. |
||